- 1. 自动计算一个分数占据结构的最佳扩胞方式并进行扩胞,可以与下面sqs的pymatgen脚本连用进行批量化操作
- 1.pymatgen检验相同结构
- 2. pymatgen-enumeration
- 3. pymatgen-orderdisorder
1. 自动计算一个分数占据结构的最佳扩胞方式并进行扩胞,可以与下面sqs的pymatgen脚本连用进行批量化操作
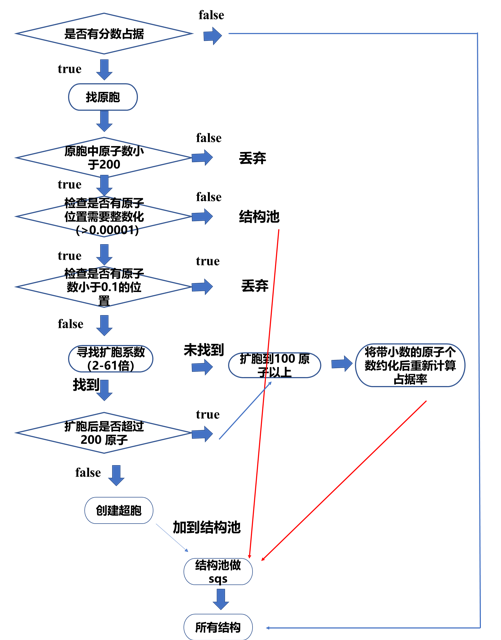
#通过修改 tolerance可以限制哪些结构扩胞到100个原子以上,这样有助于增加最后的分数占据的小数的位数
import os
import math
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.core.composition import Composition
import re
import warnings
from pymatgen.symmetry.analyzer import SpacegroupAnalyzer
import shutil
from pymatgen.core.periodic_table import Element
def get_scaling_factors(n):
"""
将整数n分解为三个尽可能接近的整数因子。
"""
if n == 1:
return [1, 1, 1]
cbrt = int(round(n**(1/3.0)))
for a in range(cbrt, 0, -1):
if n % a == 0:
rem = n // a
sqrt_rem = int(round(rem**0.5))
for b in range(sqrt_rem, 0, -1):
if rem % b == 0:
c = rem // b
factors = sorted([a, b, c], reverse=True)
return factors
return [n, 1, 1]
def get_site_contributions_from_cif(filepath):
"""
【新功能】直接从CIF文件中解析 _atom_site_ 循环,
计算每一行 (多样性 * 占有率) 的值。
Args:
filepath (str): CIF文件的路径。
Returns:
list: 包含每一行计算出的原子数的列表。如果解析失败则返回空列表。
"""
# contributions = []
site_info_list = []
try:
with open(filepath, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
except Exception as e:
print(f"错误: 无法打开文件 {filepath}. 原因: {e}")
return []
in_atom_loop = False
header_keys = []
# 正则表达式用于安全地分割可能包含带引号字符串的行
line_splitter = re.compile(r'''((?:[^ "']|"[^"]*"|'[^']*')+)''')
for line in lines:
line = line.strip()
if not line or line.startswith('#'):
continue
# 遇到 'loop_' 开始寻找 _atom_site_ 标签
if line.lower() == 'loop_':
in_atom_loop = False
header_keys = []
continue
if line.lower().startswith('_atom_site_'):
in_atom_loop = True
header_keys.append(line.lower())
continue
# 如果我们在一个原子循环中,并且已经读取了头部信息,那么这就是数据行
if in_atom_loop and header_keys:
# 如果遇到新的数据块或循环,则当前原子循环结束
if line.startswith('data_') or line.startswith('loop_') or line.startswith('_'):
in_atom_loop = False
continue
# 使用正则表达式分割行以处理带空格的标签等情况
parts = [p.strip() for p in line_splitter.split(line) if p.strip()]
if len(parts) < len(header_keys):
continue
try:
# 找到多样性和占有率所在的列索引
mult_idx = header_keys.index('_atom_site_symmetry_multiplicity')
occ_idx = header_keys.index('_atom_site_occupancy')
multiplicity = int(parts[mult_idx])
occupancy = float(parts[occ_idx])
# 计算贡献值并添加到列表
amount = multiplicity * occupancy
# contributions.append(amount)
site_info_list.append({
"multiplicity": multiplicity,
"occupancy": occupancy,
"amount": amount
})
except (ValueError, IndexError) as e:
print(f"警告: 无法解析原子位点行: '{line}'. 原因: {e}")
continue
is_fractional = False
for info in site_info_list:
occupancy = info['occupancy']
if abs(occupancy - 1.0) > 0.001:
print(f"文件 '{os.path.basename(filepath)}' 中发现分数占据位点: 占有率 {occupancy:.4f}")
is_fractional = True
break
if is_fractional:
return site_info_list
else:
print(f"文件 '{os.path.basename(filepath)}' 所有位点均为整数占据。")
all_occupied_dir = '6-all_occupied'
try:
os.makedirs(all_occupied_dir, exist_ok=True)
shutil.copy(filepath, os.path.join(all_occupied_dir, os.path.basename(filepath)))
print(f"已将文件移动到 '{all_occupied_dir}/' 目录。")
except Exception as e:
print(f"移动文件 '{filepath}' 时出错: {e}")
return []
def create_modified_cif_content(filepath, new_occupancies):
"""
读取原始CIF文件,仅替换_atom_site_loop_中的占有率值。
Args:
filepath (str): 原始CIF文件的路径。
new_occupancies (list[float]): 按顺序排列的新的占有率值。
Returns:
str: 一个包含完整CIF文件内容的字符串,如果失败则返回None。
"""
try:
with open(filepath, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
except Exception as e:
print(f"错误: 无法打开文件 {filepath}. 原因: {e}")
return []
new_cif_lines = []
in_atom_loop = False
header_keys = []
occ_idx = -1
atom_site_counter = 0
line_splitter = re.compile(r'''((?:[^ "']|"[^"]*"|'[^']*')+)''')
for line in lines:
stripped_line = line.strip()
if stripped_line.lower() == 'loop_':
in_atom_loop = False
header_keys = []
occ_idx = -1
new_cif_lines.append(line)
continue
if stripped_line.lower().startswith('_atom_site_'):
in_atom_loop = True
header_keys.append(stripped_line.lower())
new_cif_lines.append(line)
continue
# 如果我们在原子数据区
if in_atom_loop and header_keys and not stripped_line.startswith('_'):
# 第一次进入数据区时,找到占有率列的索引
if occ_idx == -1:
try:
occ_idx = header_keys.index('_atom_site_occupancy')
except ValueError:
print("错误: _atom_site_loop_ 中未找到 _atom_site_occupancy 标签。")
return None
# 分割行,替换值,然后重新组合
parts = [p for p in line_splitter.split(stripped_line) if p.strip()]
if len(parts) == len(header_keys):
if atom_site_counter < len(new_occupancies):
# 格式化新的占有率,保留足够精度
parts[occ_idx] = f"{new_occupancies[atom_site_counter]:.5f}"
# 重新组合成一行,注意保留原始的空格格式
# 这是一个简化处理,假设列之间是单个或多个空格
new_line = " ".join(parts) + "\n"
new_cif_lines.append(new_line)
atom_site_counter += 1
else:
print('占用率列表不够长')
else:
print('行格式不匹配')
else:
if stripped_line.startswith('_') and in_atom_loop:
in_atom_loop = False # 遇到新的标签,原子循环结束
new_cif_lines.append(line)
if not os.path.exists('3-intermediate_dir'):
os.makedirs('3-intermediate_dir')
base_name = os.path.basename(filepath)
file_name_without_ext = os.path.splitext(base_name)[0]
intermediate_filename = f"{file_name_without_ext}_modified.cif"
intermediate_filepath = os.path.join('3-intermediate_dir', intermediate_filename)
with open(intermediate_filepath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("".join(new_cif_lines))
print(f"成功保存修正后的中间文件: {intermediate_filepath}")
return "".join(new_cif_lines)
#针对8个位点0.07占据 的情况的处理,先扩胞到100个原子以上,然后约化原子个数,然后重新反除回去,然后把点位的分数占据重新计算,然后再扩胞
def process_via_text_modification(filepath):
print(f"--- 正在处理文件 (文本模式): {os.path.basename(filepath)} ---")
output_dir = '4-appro_structures'
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
# 步骤1: 解析文本获取原子位点信息
site_info = get_site_contributions_from_cif(filepath)
if not site_info:
print(f"无法从 {filepath} 解析原子位点信息")
return
contributions = [info['amount'] for info in site_info]
initial_total_atoms = sum(contributions)
print(f"单胞中的初始总原子数: {initial_total_atoms:.4f}")
best_n = None
for n in range(1, 61):
if initial_total_atoms * n >= 100:
best_n = n
break
print(f"找到合适的扩胞倍数 n = {best_n}")
# 步骤3: 计算所有位点的新占有率
new_occupancies = []
for info in site_info:
scaled_amount_rounded = round(info['amount'] * best_n)
if info['multiplicity'] == 0 or best_n == 0:
new_occ = 0
else:
new_occ = scaled_amount_rounded / (info['multiplicity'] * best_n)
new_occupancies.append(new_occ)
# 步骤4: 生成包含新占有率的CIF文件内容(纯文本操作)
modified_cif_content = create_modified_cif_content(filepath, new_occupancies)
try:
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter("ignore", UserWarning)
modified_structure = Structure.from_str(modified_cif_content, fmt="cif")
except Exception as e:
print(f"错误: Pymatgen无法得到结构")
return
scaling_factors = get_scaling_factors(best_n)
supercell = modified_structure.copy()
supercell.make_supercell(scaling_factors)
# 步骤6: 保存最终的超胞结构
base_name = os.path.basename(filepath)
file_name_without_ext = os.path.splitext(base_name)[0]
scaling_str = f"{scaling_factors[0]}{scaling_factors[1]}{scaling_factors[2]}"
output_filename = f"{file_name_without_ext}_scaled_{scaling_str}.cif"
output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, output_filename)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter("ignore", UserWarning)
supercell.to(fmt="cif", filename=output_path)
print(f"成功创建并保存超胞: {output_path}")
print(f"最终超胞化学式: {supercell.composition.reduced_formula},总原子数: {supercell.num_sites}\n")
def process_structure_file(filepath, output_dir, tolerance=0.00001):
"""
处理单个CIF文件,根据每个位点的原子贡献判断是否需要扩胞,并执行扩胞操作。
"""
print(f"--- 正在处理文件: {filepath} ---")
# 【新流程】首先从CIF文本中直接解析每个位点的原子数贡献
site_info_list = get_site_contributions_from_cif(filepath)
if site_info_list == []:
return
site_amounts = [info['amount'] for info in site_info_list]
total_sum = sum(site_amounts)
if not site_amounts:
print(f"错误: 未能从 {filepath} 的 _atom_site_ 循环中提取到数据。")
return
try:
structure = Structure.from_file(filepath)
except Exception as e:
print(f"错误: Pymatgen无法读取或解析文件 {filepath}. 原因: {e}")
return
analyzer = SpacegroupAnalyzer(structure)
prim_cell = analyzer.find_primitive()
structur_site_num = structure.num_sites
prim_site_num = prim_cell.num_sites
if prim_site_num != structur_site_num:
n_scal = structur_site_num / prim_site_num
print(f'单胞是原胞的{n_scal}倍')
site_amounts = [amount / n_scal for amount in site_amounts]
total_sum = total_sum / n_scal
if not os.path.exists('1-exceed_200'):
os.makedirs('1-exceed_200')
if total_sum >= 200:
shutil.copy(filepath, os.path.join('1-exceed_200', os.path.basename(filepath)))
print('原胞中原子个数超过200个原子,跳过')
return
print(f"从CIF中解析出的各行原子数贡献: {[round(x, 4) for x in site_amounts]}")
# 检查是否有任何一个位点贡献值需要进行整数化处理
needs_scaling = False
for amount in site_amounts:
if abs(amount - round(amount)) > tolerance:
needs_scaling = True
print(f"位点贡献值 {round(amount, 4)} 与整数偏差大于 {tolerance}。")
break
if not needs_scaling:
print("该结构所有位点贡献值均在容差范围内,无需扩胞。")
# if total_sum > 200:
# print('虽然无需扩胞,但是该结构总原子数超过200个原子,将进行约化处理')
# # shutil.copy(filepath, os.path.join(need_appro_dir, os.path.basename(filepath)))
# process_via_text_modification(filepath)
# return
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
base_name = os.path.basename(filepath)
file_name_without_ext = os.path.splitext(base_name)[0]
output_filename = f"{file_name_without_ext}_scaled_111.cif" # 固定后缀
output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, output_filename)
# 保存原胞到新路径
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter("ignore", UserWarning)
prim_cell.to(fmt="cif", filename=output_path)
print(f"已将结构保存至: {output_path}\n")
return
# analyzer = SpacegroupAnalyzer(structure)
# prim_cell = analyzer.find_primitive()
# structur_site_num = structure.num_sites
# prim_site_num = prim_cell.num_sites
# if prim_site_num != structur_site_num:
# n_scal = structur_site_num / prim_site_num
# print(f'单胞是原胞的{n_scal}倍')
# site_amounts = [amount / n_scal for amount in site_amounts]
# total_sum = total_sum / n_scal
# 如果需要扩胞,寻找最小的扩胞系数 (从2到10)
best_scaling_factor = None
for n in range(2, 61):
is_factor_suitable = True
for amount in site_amounts: # 使用从CIF解析出的列表进行检查
scaled_amount = amount * n
if abs(scaled_amount - round(scaled_amount)) > tolerance:
is_factor_suitable = False
break
if is_factor_suitable:
best_scaling_factor = n
print(f"找到合适的扩胞系数: {n}")
break
#如果有原子个数小于0.1的位点,后续sqs或order很难做,所以在这里收集起来,后续直接修改占据数或者舍弃
best_scaling_atom = site_amounts * n
lessthan1 = False
for site_number in best_scaling_atom:
if site_number < 0.1:
print(f"文件 '{os.path.basename(filepath)}' 中发现有原子个数小于0.1")
lessthan1 = True
break
if lessthan1:
os.makedirs('5-lessthan1dir', exist_ok=True)
shutil.copy(filepath, os.path.join('5-lessthan1dir', os.path.basename(filepath)))
print("已将文件移动到 '5-lessthan1dir/' 目录。")
return
if best_scaling_factor is None:
print(f"{filepath}在2-60倍范围内未找到合适的扩胞系数,将进行约化处理")
process_via_text_modification(filepath)
# shutil.copy(filepath, os.path.join(need_appro_dir, os.path.basename(filepath)))
return
# 使用Pymatgen读取结构,用于执行扩胞操作
# try:
# structure = Structure.from_file(filepath)
# except Exception as e:
# print(f"错误: Pymatgen无法读取或解析文件 {filepath}. 原因: {e}")
# return
# 计算扩胞矩阵并创建超胞
scaling_factors = get_scaling_factors(best_scaling_factor)
total_atom_number = total_sum * best_scaling_factor
if total_atom_number > 200:
print('该结构总原子数超过200个原子')
print(f'该结构总原子数为{total_atom_number},将进行约化处理')
# shutil.copy(filepath, os.path.join(need_appro_dir, os.path.basename(filepath)))
process_via_text_modification(filepath)
return
supercell = prim_cell.copy()
supercell.make_supercell(scaling_factors)
# for i, site in enumerate(supercell.sites):
# # site.specie.symbol 获取元素的符号 (如 'Li', 'Mg')
# # i 是从0开始的索引,我们加1让它从1开始
# # f"{...}" 是Python的格式化字符串
# site.label = f"{site.species.symbol}{i+1}"
# print("标签重新生成完毕。")
# 保存扩胞后的结构
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
base_name = os.path.basename(filepath)
file_name_without_ext = os.path.splitext(base_name)[0]
scaling_str = f"{scaling_factors[0]}{scaling_factors[1]}{scaling_factors[2]}"
output_filename = f"{file_name_without_ext}_scaled_{scaling_str}.cif"
output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, output_filename)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter("ignore", UserWarning)
supercell.to(fmt="cif", filename=output_path)
# supercell.to(fmt="cif", filename=output_path)
print(f"成功创建超胞,并保存至: {output_path}")
print(f"新结构的化学式: {supercell.composition.reduced_formula}\n")
if __name__ == '__main__':
input_dir = './rawdata/all_randomized_cifs'
for file in os.listdir(input_dir):
if file.endswith(".cif"):
test_filename = os.path.join(input_dir, file)
process_structure_file(test_filename, output_dir="2-output_structures")
1.pymatgen检验相同结构
fcc、bcc等对应着特殊空间群里特定位置的占据
1.一次性检验
import os
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.sets import batch_write_input, MPRelaxSet
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
standard_structures= []
dir='./'
for i in range(1000):
filename = "{}.vasp".format(i)
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(dir,filename)):
continue
print(filename)
structure = Structure.from_file(filename)
structure.remove_species("O")
standard_structures.append(structure)
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d for d in standard_structures])
print(len(groups))
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups] # 将嵌套列表的每个列表的第一个元素提取出来做成一个新列表
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = 0
for Cry_Str in groupstructures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%dnew.vasp'%n)
2.逐个检验
import numpy as np
import sys,os,time
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
all_str = []
for i in range(1,100000):
file = f'{i}.vasp'
if not os.path.exists(file):
continue
print(file)
strua = Structure.from_file(file)
match_found = False
for str in all_str:
if matcher.fit(strua,str):
match_found = True
break
if not match_found:
all_str.append(strua)
print('%d structures' % len(all_str))
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = 0
for strua in all_str:
Vasp_Str = Poscar(strua)
n +=1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%dnew.vasp'%n)
3. 检验两个结构
import numpy as np
import sys,os,time
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
aa = Structure.from_file('16.vasp')
bb = Structure.from_file('4199.vasp')
matcher.fit(aa,bb)
2. pymatgen-enumeration
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.symmetry.analyzer import SpacegroupAnalyzer
from pymatgen.transformations.advanced_transformations import EnumerateStructureTransformation
from pymatgen.io.vasp.sets import batch_write_input, MPRelaxSet
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
from pymatgen.analysis.bond_valence import BVAnalyzer
structure = Structure.from_file("a.cif")
data = {"Na":1, "Y":3, "Si":4,"O":-2,"Al":3,"K":1}
analyzer = SpacegroupAnalyzer(structure)
prim_cell = analyzer.find_primitive()
prim_cell.add_oxidation_state_by_element(data)
#print(prim_cell)
enum = EnumerateStructureTransformation()
enumerated = enum.apply_transformation(prim_cell, 100)
structures = [d["structure"] for d in enumerated]
print("%d structures returned." % len(structures))
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = 0
for Cry_Str in structures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%n)
#from pymatgen.io.cif import CifWriter
#n = 0
#for Cry_Str in structures:
# n = n + 1
# cif_filename = f"{n}.cif"
# cif_writer = CifWriter(Cry_Str)
# cif_writer.write_file(cif_filename)
#energy= [d["energy"] for d in enumerated]
#fl = open('energy.dat','w')
#fl.writelines(str(energy))
#data = {"K":1, "O":-2, "Fe":2,"Ti":4.25,"Mn":3.75}
#abc=[]
#for i in range(1,101):
# m = Structure.from_file('%d.vasp'%i)
# m.add_oxidation_state_by_element(data)
# energy = EwaldElectrostaticModel().get_energy(m)
# abc.append(energy)
#f2 = open('energy2.dat','w')
#f2.writelines(str(abc))
with open('energy.dat', 'w') as f:
for item in abc:
f.write(str(item) + '\n')
#strcturelist2.sort(key = EwaldElectrostaticModel().get_energy)
3. pymatgen-orderdisorder
import os
from pymatgen.io.cif import CifParser, CifWriter
from pymatgen.transformations.standard_transformations import SubstitutionTransformation, OrderDisorderedStructureTransformation, SupercellTransformation
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.symmetry.analyzer import SpacegroupAnalyzer
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
from pymatgen.transformations.advanced_transformations import EnumerateStructureTransformation
from pymatgen.io.vasp.sets import batch_write_input, MPRelaxSet
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
structure = Structure.from_file("a.cif")
data = {"Ni":2, "Co":3, "S":-2,"Se":-2}
analyzer = SpacegroupAnalyzer(structure)
prim_cell = analyzer.find_primitive()
prim_cell.add_oxidation_state_by_element(data)
print(prim_cell)
order = OrderDisorderedStructureTransformation()
standard_structures=order.apply_transformation(prim_cell,return_ranked_list=1000)
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d["structure"] for d in standard_structures]) #这应该是个字典,把字典中的structure关键字提出来组>成列表,groups里只剩下结构了
#structures = [d["structure"] for d in standard_structures]
#print("%d structures returned." % len(structures))
#from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
#n = 0
#for Cry_Str in structures:
#print(Cry_Str)
# Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
# n = n+1
# Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%n)
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups] # 将嵌套列表的每个列表的第一个元素提取出来做成一个新列表
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = 0
for Cry_Str in groupstructures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%n)
#产生等差数列 for i in range(len(groups))
#提取出列举时计算的能量 energy = [x('energy') for x in standard_structures]
#验证同一类群下的结构静电能相等
#suoyoua = [x for x in groups[0]]
#for cry in suoyoua:
# energy = EwaldElectrostaticModel().get_energy(cry)
# print(energy)
#验证输出的顺序是按照能量升序进行的
#suoyou1 = [x[0] for x in groups]
#for cry in suoyou1:
# energy = EwaldElectrostaticModel().get_energy(cry)
# print(energy)
批量做
import os
from pymatgen.transformations.standard_transformations import OrderDisorderedStructureTransformation
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
structure = Structure.from_file("a.cif")
COMMON_OXIDATION_STATES = {
'H': 1, 'He': 0, 'Li': 1, 'Be': 2, 'B': 3, 'C': 4, 'N': -3, 'O': -2, 'F': -1,
'Ne': 0, 'Na': 1, 'Mg': 2, 'Al': 3, 'Si': 4, 'P': 5, 'S': -2, 'Cl': -1, 'Ar': 0,
'K': 1, 'Ca': 2, 'Sc': 3, 'Ti': 4, 'V': 5, 'Cr': 3, 'Mn': 2, 'Fe': 3, 'Co': 2,
'Ni': 2, 'Cu': 2, 'Zn': 2, 'Ga': 3, 'Ge': 4, 'As': 3, 'Se': -2, 'Br': -1, 'Kr': 0,
'Rb': 1, 'Sr': 2, 'Y': 3, 'Zr': 4, 'Nb': 5, 'Mo': 6, 'Tc': 7, 'Ru': 4, 'Rh': 3,
'Pd': 2, 'Ag': 1, 'Cd': 2, 'In': 3, 'Sn': 4, 'Sb': 3, 'Te': -2, 'I': -1, 'Xe': 0,
'Cs': 1, 'Ba': 2, 'La': 3, 'Ce': 3, 'Pr': 3, 'Nd': 3, 'Pm': 3, 'Sm': 3, 'Eu': 3,
'Gd': 3, 'Tb': 3, 'Dy': 3, 'Ho': 3, 'Er': 3, 'Tm': 3, 'Yb': 3, 'Lu': 3, 'Hf': 4,
'Ta': 5, 'W': 6, 'Re': 4, 'Os': 4, 'Ir': 4, 'Pt': 4, 'Au': 3, 'Hg': 2, 'Tl': 1,
'Pb': 2, 'Bi': 3, 'Po': 2, 'At': -1, 'Rn': 0, 'Fr': 1, 'Ra': 2, 'Ac': 3, 'Th': 4,
'Pa': 5, 'U': 6, 'Np': 5, 'Pu': 4, 'Am': 3, 'Cm': 3, 'Bk': 3, 'Cf': 3, 'Es': 3,
'Fm': 3, 'Md': 3, 'No': 2, 'Lr': 3
}
# structure.add_oxidation_state_by_guess()
oxi_states_for_structure = {
el.symbol: COMMON_OXIDATION_STATES.get(el.symbol)
for el in structure.composition.elements
if el.symbol in COMMON_OXIDATION_STATES
}
structure.add_oxidation_state_by_element(oxi_states_for_structure)
order = OrderDisorderedStructureTransformation()
standard_structures=order.apply_transformation(structure,return_ranked_list=2)
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d["structure"] for d in standard_structures]) #这应该是个字典,把字典中的structure关键字提出来组>成列表,groups里只剩下结构了
#structures = [d["structure"] for d in standard_structures]
#print("%d structures returned." % len(structures))
#from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
#n = 0
#for Cry_Str in structures:
#print(Cry_Str)
# Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
# n = n+1
# Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%n)
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups] # 将嵌套列表的每个列表的第一个元素提取出来做成一个新列表
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = 0
for Cry_Str in groupstructures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%n)
4.计算静电能
import os
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
abc=[]
data = {"Ca":-6, "H":1}
for i in range(1,5034):
m = Structure.from_file('%d.vasp'%i)
m.add_oxidation_state_by_element(data)
energy = EwaldElectrostaticModel().get_energy(m)
abc.append(energy)
with open('energy.dat', 'w') as f:
for item in abc:
f.write(str(item) + '\n')
5. sqs
使用pymatgen进行sqs操作
需要安装好ATAT
from pymatgen.core import Structure,Composition
from pymatgen.transformations.advanced_transformations import SQSTransformation
import os
path_a = os.getcwd()
print(path_a)
os.makedirs('sqs_debug_folder', exist_ok=True)
s_original = Structure.from_file("a.cif")
new_species_list = []
for site in s_original.sites:
current_species_dict = site.species.get_el_amt_dict()
total_occupancy = sum(current_species_dict.values())
if 0 < total_occupancy < 1.0:
vacancy_fraction = 1.0 - total_occupancy
current_species_dict['X'] = vacancy_fraction
new_species_list.append(Composition(current_species_dict))
s_for_sqs = Structure(s_original.lattice, new_species_list, s_original.frac_coords)
trans = SQSTransformation(
scaling=[1,1,1],
sqs_method="mcsqs",
instances=1,
search_time=3,
cluster_size_and_shell = {2: 2, 3: 1},
reduction_algo=False,
directory="./sqs_debug_folder"
)
sqs_with_dummies = trans.apply_transformation(s_for_sqs)
sqs_final = sqs_with_dummies.copy()
sqs_final.remove_species(["X"])
output_filepath = os.path.join(path_a, 'sqs_mcsqs.cif')
sqs_final.to(fmt="cif", filename=output_filepath)



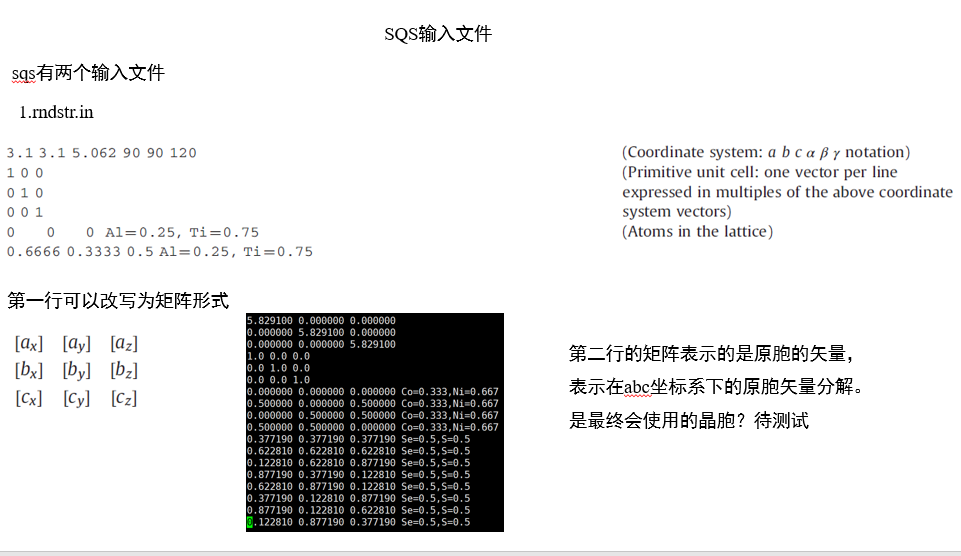




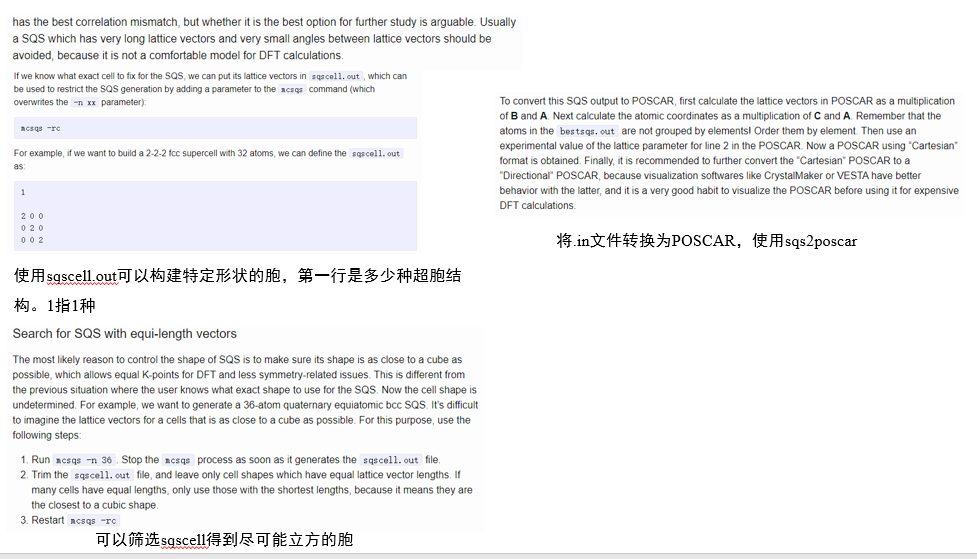


1.前处理
1. 转换rndstr格式的结构
from pymatgen.core import Structure
structure = Structure.from_file("a.cif")
structure.to(filename='rndstr.in')
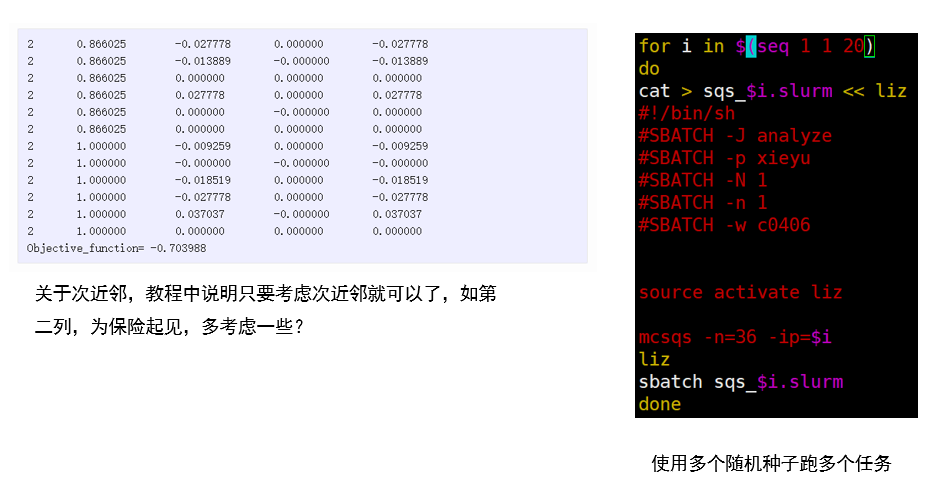
2.提交多个ip的任务
for i in $(seq 1 1 20)
do
cat > sqs_$i.slurm << liz
#!/bin/sh
#SBATCH -J analyze
#SBATCH -p xieyu
#SBATCH -N 1
#SBATCH -n 1
#SBATCH -w c0406
source activate liz
mcsqs -n=36 -ip=$i
liz
sbatch sqs_$i.slurm
done
#grep Objective_function bestcorr*.out|sort -n
2. 后处理
1. 提取bestcorr
for i in $(seq 1 1 12)
do
tail -n 1 bestcorr.out >> corr.dat
done
2.对多任务ip产生的best.out文件处理
==注意,数字前的空格会对结构在vesta中的显示产生影响==
sqs2poscar文件在 同步空间/计算脚本/sqs处
for i in $(seq 1 1 12)
do
./sqs2poscar bestsqs$i.out
mv bestsqs$i.out-POSCAR $i.vasp
sed -i '2s/.*/1/' $i.vasp
sed -i '3s/-10\.57524/ -10.57524/' $i.vasp
done
3. 检验相同的结构
import os
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.sets import batch_write_input, MPRelaxSet
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
standard_structures= []
for i in range(1,13):
filename = "{}.vasp".format(i)
print(filename)
structure = Structure.from_file(filename)
standard_structures.append(structure)
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d for d in standard_structures]) #这应该是个字典,把字典中的structure关键字提出来组成列表,groups里只剩下结构了
#structures = [d["structure"] for d in standard_structures]
#print("%d structures returned." % len(structures))
#from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
#n = 0
#for Cry_Str in structures:
#print(Cry_Str)
# Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
# n = n+1
# Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%n)
print(len(groups))
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups] # 将嵌套列表的每个列表的第一个元素提取出来做成一个新列表
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = 0
for Cry_Str in groupstructures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%dnew.vasp'%n)
#产生等差数列 for i in range(len(groups))
#提取出列举时计算的能量 energy = [x('energy') for x in standard_structures]
#验证同一类群下的结构静电能相等
#suoyoua = [x for x in groups[0]]
#for cry in suoyoua:
# energy = EwaldElectrostaticModel().get_energy(cry)
# print(energy)
#验证输出的顺序是按照能量升序进行的
#suoyou1 = [x[0] for x in groups]
#for cry in suoyou1:
# energy = EwaldElectrostaticModel().get_energy(cry)
# print(energy)
6.暴力枚举
1.枚举脚本
在替换多种元素时,可以只替换一种元素,然后在生成的poscar中直接修改元素种类和个数
#!/usr/bin/python2
#Change the format of crystal structure
#python Str_Format.py infile outfile
try:
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
except:
print ('You should install pymatgen first.')
exit(0)
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
def readvasp(infile):
with zopen(infile, "rt") as f:
contents = f.read()
Cry_Str = IStructure.from_str(contents, fmt="poscar")
lattice = Cry_Str.lattice
species = [ x.species.elements[0] for x in Cry_Str.sites ]
coords = [ x.coords for x in Cry_Str.sites ]
Cry_Str = Structure(lattice,species,coords,coords_are_cartesian=True)
return Cry_Str
def replace(Cry_Str, replace_list, outfile):
natom = len(Cry_Str.sites)
for ele in replace_list:
for i in ele[0]:
Cry_Str.replace(i,ele[1])
Cry_Str.sort()
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str.write_file(outfile)
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
instr = 'a.vasp'
Cry_Str = readvasp(instr)
#modify
Cry_Str.make_supercell([1,1,1])
for i in range(10):
Cry_tp = Cry_Str.copy()
re_index = np.arange(28,82)
np.random.shuffle(re_index)
re_index1 = re_index[:3]
re_index2 = re_index[7:9]
replace_list = [ [re_index1, 'B'],[re_index2,'O'] ]
tmp = '%d.vasp'%i
replace(Cry_tp, replace_list, tmp)
2. 多任务脚本 检验相同结构
for i in $(seq 0 1000 25000)
do
cat > job_$i.sh << liz
#!/bin/sh
#SBATCH -J liz
#SBATCH -p xieyu
#SBATCH -N 1
#SBATCH -n 1
#SBATCH -w c0607
source activate liz
python jianyan_$i.py
liz
cat > jianyan_$i.py << liz
import os
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.sets import batch_write_input, MPRelaxSet
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
standard_structures= []
dir='/work/home/liz/workspace/D-LuNH-sqs/2-Lu-25电子/1-暴力破解/3-zuhe'
for i in range($i,$((i+1000))):
filename = "{}.vasp".format(i)
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(dir,filename)):
continue
print(filename)
structure = Structure.from_file(filename)
standard_structures.append(structure)
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d for d in standard_structures])
print(len(groups))
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups] # 将嵌套列表的每个列表的第一个元素提取出来做成一个新列表
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = $i
for Cry_Str in groupstructures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%dnew.vasp'%n)
liz
sbatch job_$i.sh
done
3.改良版
1.限定最小距离
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
strua = Structure.from_file("a.vasp")
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]])
#print(strua.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[1]))
#a_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[0]].frac_coords
#b_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords
#c_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[2]].frac_coords
#arr1=a_frac_coords-b_frac_coords
#arr1[arr1 >= 0.5] = 1
#arr1[arr1 <= -0.5] = -1
#arr1[np.logical_and(arr1 > -0.5, arr1 < 0.5)] = 0
#print(arr1)
#strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords +=arr1
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]])
#print(strua.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[1]))
#diff1=np.sqrt(np.dot(strua.sites[re_index1[0]].coords-strua.sites[re_index1[1]].coords,strua.sites[re_index1[0]].coords-strua.sites[re_index1[1]].coords))
#if diff1<3
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords)
#h2=a_frac_coords-c_frac_coords
#h3=b_frac_coords-c_frac_coords
#lattice = strua.lattice
#lattice_matrix =np.array(lattice.matrix)
#coords = [ x.coords for x in strua.sites ]
#矩阵乘法 np.dot(A,B)
#矩阵改变维数 A.reshape(1,3)
#sites从0开始
#np.dot(a,a)求平方和
#strua.sites[0].coords 输出笛卡尔坐标 .frac_coords分数坐标
#print(np.sqrt(np.dot(strua.sites[70].coords-strua.sites[71].coords,strua.sites[70].coords-strua.sites[71].coords)))
#求两个原子的距离
for i in range(20):
Cry_tp = strua.copy()
re_index = np.arange(27,82)
np.random.shuffle(re_index)
re_index1 = re_index[:3]
replace_list = [ [re_index1, 'N'] ]
if Cry_tp.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[1])<3.6 or Cry_tp.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[2])<3.6 or Cry_tp.get_distance(re_index1[1],re_index1[2])<3.6:
continue
for ele in replace_list:
for j in ele[0]:
Cry_tp.replace(j,ele[1])
Cry_tp.sort()
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_tp)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%i)
2.限定最小距离且保证替代发生在不同的位置
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
strua = Structure.from_file("a.vasp")
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]])
#print(strua.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[1]))
#a_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[0]].frac_coords
#b_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords
#c_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[2]].frac_coords
#arr1=a_frac_coords-b_frac_coords
#arr1[arr1 >= 0.5] = 1
#arr1[arr1 <= -0.5] = -1
#arr1[np.logical_and(arr1 > -0.5, arr1 < 0.5)] = 0
#print(arr1)
#strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords +=arr1
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]])
#print(strua.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[1]))
#diff1=np.sqrt(np.dot(strua.sites[re_index1[0]].coords-strua.sites[re_index1[1]].coords,strua.sites[re_index1[0]].coords-strua.sites[re_index1[1]].coords))
#if diff1<3
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords)
#h2=a_frac_coords-c_frac_coords
#h3=b_frac_coords-c_frac_coords
#lattice = strua.lattice
#lattice_matrix =np.array(lattice.matrix)
#coords = [ x.coords for x in strua.sites ]
#矩阵乘法 np.dot(A,B)
#矩阵改变维数 A.reshape(1,3)
#sites从0开始
#np.dot(a,a)求平方和
#strua.sites[0].coords 输出笛卡尔坐标 .frac_coords分数坐标
#print(np.sqrt(np.dot(strua.sites[70].coords-strua.sites[71].coords,strua.sites[70].coords-strua.sites[71].coords)))
#求两个原子的距离
for i in range(20):
Cry_tp = strua.copy()
re_index = np.arange(27,108)
np.random.shuffle(re_index)
re_index1 = re_index[:3]
if all(27<= num <=53 for num in re_index1):
continue
if all(54<= num <=107 for num in re_index1):
continue
replace_list = [ [re_index1, 'N'] ]
if Cry_tp.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[1])<3.6 or Cry_tp.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[2])<3.6 or Cry_tp.get_distance(re_index1[1],re_index1[2])<3.6:
continue
for ele in replace_list:
for j in ele[0]:
Cry_tp.replace(j,ele[1])
Cry_tp.sort()
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_tp)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%i)
3.限定空间群
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.symmetry.analyzer import SpacegroupAnalyzer
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
strua = Structure.from_file("a.vasp")
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]])
#print(strua.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[1]))
#a_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[0]].frac_coords
#b_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords
#c_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[2]].frac_coords
#arr1=a_frac_coords-b_frac_coords
#arr1[arr1 >= 0.5] = 1
#arr1[arr1 <= -0.5] = -1
#arr1[np.logical_and(arr1 > -0.5, arr1 < 0.5)] = 0
#print(arr1)
#strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords +=arr1
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]])
#print(strua.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[1]))
#diff1=np.sqrt(np.dot(strua.sites[re_index1[0]].coords-strua.sites[re_index1[1]].coords,strua.sites[re_index1[0]].coords-strua.sites[re_index1[1]].coords))
#if diff1<3
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords)
#h2=a_frac_coords-c_frac_coords
#h3=b_frac_coords-c_frac_coords
#lattice = strua.lattice
#lattice_matrix =np.array(lattice.matrix)
#coords = [ x.coords for x in strua.sites ]
#矩阵乘法 np.dot(A,B)
#矩阵改变维数 A.reshape(1,3)
#sites从0开始
#np.dot(a,a)求平方和
#strua.sites[0].coords 输出笛卡尔坐标 .frac_coords分数坐标
#print(np.sqrt(np.dot(strua.sites[70].coords-strua.sites[71].coords,strua.sites[70].coords-strua.sites[71].coords)))
#求两个原子的距离
total_structure=[]
for i in range(200000):
Cry_tp = strua.copy()
re_index = np.arange(0,96)
np.random.shuffle(re_index)
re_index1 = re_index[:4]
Cry_tp.remove_sites(re_index1)
a=SpacegroupAnalyzer(Cry_tp).get_space_group_number()
if a<= 140:
continue
print(i)
print(a)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_tp)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%i)
total_structure.append(Cry_tp)
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d for d in total_structure])
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups]
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = 10001
for Cry_Str in groupstructures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%dnew.vasp'%n)
4.多任务做改良版
for i in $(seq 1 100 10100)
do
cat > baoli_$i.py << liz
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.symmetry.analyzer import SpacegroupAnalyzer
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
strua = Structure.from_file("a.vasp")
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]])
#print(strua.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[1]))
#a_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[0]].frac_coords
#b_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords
#c_frac_coords=strua.sites[re_index1[2]].frac_coords
#arr1=a_frac_coords-b_frac_coords
#arr1[arr1 >= 0.5] = 1
#arr1[arr1 <= -0.5] = -1
#arr1[np.logical_and(arr1 > -0.5, arr1 < 0.5)] = 0
#print(arr1)
#strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords +=arr1
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]])
#print(strua.get_distance(re_index1[0],re_index1[1]))
#diff1=np.sqrt(np.dot(strua.sites[re_index1[0]].coords-strua.sites[re_index1[1]].coords,strua.sites[re_index1[0]].coords-strua.sites[re_index1[1]].coords))
#if diff1<3
#print(strua.sites[re_index1[1]].frac_coords)
#h2=a_frac_coords-c_frac_coords
#h3=b_frac_coords-c_frac_coords
#lattice = strua.lattice
#lattice_matrix =np.array(lattice.matrix)
#coords = [ x.coords for x in strua.sites ]
#矩阵乘法 np.dot(A,B)
#矩阵改变维数 A.reshape(1,3)
#sites从0开始
#np.dot(a,a)求平方和
#strua.sites[0].coords 输出笛卡尔坐标 .frac_coords分数坐标
#print(np.sqrt(np.dot(strua.sites[70].coords-strua.sites[71].coords,strua.sites[70].coords-strua.sites[71].coords)))
#求两个原子的距离
total_structure=[]
for i in range(20000):
Cry_tp = strua.copy()
re_index = np.arange(0,96)
np.random.shuffle(re_index)
re_index1 = re_index[:4]
Cry_tp.remove_sites(re_index2)
a=SpacegroupAnalyzer(Cry_tp).get_space_group_number()
if a<= 140:
continue
print(i)
print(a)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_tp)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%i)
total_structure.append(Cry_tp)
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d for d in total_structure])
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups]
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = $((i))
for Cry_Str in groupstructures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%dnew.vasp'%n)
liz
done
4.使用枚举方法处理蓝钻结构
- 这是第一次系统使用暴力枚举法产生结构,其中,由于pymatgen用于计算ewald加和的程序太慢,使用了组内ARES中用于计算ewald能量的脚本ewalds.x
- 一共有两种方式产生,一种是完全随机的,另一种相当于对整个分子的替代(使用了pymatgen中找原子附近其他原子的功能
- 脚本、流程都经过了反复的改进
1.完全随机的方法(完全解放双手了)
- 一共需要四个文件
a.vasp
multitask.sh
ewalds.x
changeatom.py:用于产生随机的结构
以及一个后处理文件
get-all.sh
2.分为三级别目录
一级: 1-21
二级: 1-48
三级: 1-random 2-low ;其中 1-random是随机产生的结构,并计算了静电能,2-low是能量最低的前30个结构以及对应的能量
- 通过设置不同的价态,可以得到不同种原子靠近或者远离的结构
流程(产生1000万个随机结构):
1. 提任务
for i in $(seq 1 1 10);do mkdir $i;cp a.vasp ewalds.x multitask.sh changeatom.py $i;cd $i; ./multitask.sh ;cd ..;done
2. changeatom.py
需要更改的地方是产生结构的数量、以及替换的种类和位置
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
strua = Structure.from_file("a.vasp")
#需要考虑
for i in range(10000):
print(i)
Cry_tp = strua.copy()
re_index = np.arange(0,512)
np.random.shuffle(re_index)
re_index1 = re_index[:7]
re_index2 = re_index[7:9]
replace_list = [ [re_index1, 'B'],[re_index2,'O'] ]
for ele in replace_list:
for j in ele[0]:
Cry_tp.replace(j,ele[1])
Cry_tp.sort()
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_tp)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%i)
3. multitask.sh :做一些文件夹 ,提交产生结构的任务,提交计算ewald能量的任务
需要注意的是,使用ewalds.x需要先source环境
for i in $(seq 1 1 48)
do
mkdir $i
cd $i
mkdir 1-random 2-low
cd ..
cp changeatom.py $i/1-random
cp ewalds.x $i/1-random
cp a.vasp $i/1-random
cd $i/1-random
cat > job.slurm << liz
#!/bin/sh
#SBATCH --job-name=opt
#SBATCH --output=log.out.%j
#SBATCH --error=log.err.%j
#SBATCH --partition=xieyu
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1
source activate liz
python changeatom.py > log 2>&1
liz
sbatch job.slurm
cd ..
cd ..
done
sleep 1m
for i in $(seq 1 1 48)
do
cd $i/1-random
cat > ewaldenergy.slurm <<liz2
#!/bin/sh
#SBATCH --job-name=opt
#SBATCH --output=log.out.%j
#SBATCH --error=log.err.%j
#SBATCH --partition=xieyu
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1
source /work/env/intel2020
for j in \$(seq 0 1 9999);
do
echo -n \$j.vasp >> energy.dat
./ewalds.x \$j.vasp 3 5 -2 >> energy.dat
done
sort -k3n energy.dat > ewaldenergy.dat
head -n 30 ewaldenergy.dat > ../2-low/ewaldenergy.dat
head -n 30 ewaldenergy.dat | awk '{print \$1}' | while read -r line; do
cp "\$line" ../2-low/
done
liz2
sbatch ewaldenergy.slurm
cd ..
cd ..
done
4. 后处理文件 get-all.sh 提取能量最低的结构
rm all-sorted.dat
for i in $(seq 1 1 21)
do
cd $i
for j in $(seq 1 1 48)
do
cd $j
cd 2-low
#awk -v var="$j" '{ $1 = var " " $1 } 1' ewaldenergy.dat > data.dat
awk -v var="$i" -v var2="$j" '{ $1 = var " " var2 " " $1 } 1' ewaldenergy.dat > data.dat
cat data.dat >> ../../data.dat
rm data.dat
cd ..
cd ..
done
cd ..
done
for h in $(seq 1 1 21)
do
cat $h/data.dat >> ./all.dat
rm $h/data.dat
done
sort -k5n all.dat > all-sorted.dat
rm all.dat
echo 'sucess1'
# 设置计数器
count=1
rm -r all
mkdir all
# 读取包含三列信息的文件
head -n 100 all-sorted.dat | while read -r line; do
# 提取大目录、小目录和文件名
directory=$(echo "$line" | awk '{print $1}')
subdirectory=$(echo "$line" | awk '{print $2}')
filename=$(echo "$line" | awk '{print $3}')
# 构建目标文件名
target_filename="${count}_${directory}_${subdirectory}_${filename}.vasp"
# 复制文件到当前目录并重命名
cp "${directory}/${subdirectory}/2-low/${filename}" "./all/${target_filename}"
# 增加计数器
((count++))
done
echo 'sucess2'
2. 替换为B_3O和B_4O构型的方法(还需要手动做一些流程)
- 替换为特定构型的方法利用了pymatgen中寻找相邻原子的方法,基本的流程是
先随机找两个可能替换氧原子的位置
检验氧原子的距离是否符合要求(在本例中设定两个氧原子不要靠的太近,以免产生O-B-O键
查找两个位置附近的原子的位置
替换附近原子为B
检验相同结构
计算静电能
- 另一套流程是:(下文的流程)
先随机替换氧的位置
检验氧原子距离
检验氧的相同结构
替换B
检验相同结构
计算静电能
这样流程的好处是可以大大减少产生结构的数量,缺点是不能把算能量的步骤集成
- 值得注意的一点是,在这次的产生结构的脚本中,是可以枚举O的所有可能情况的,所以最终结果是枚举的

1. 枚举氧的位置
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
from itertools import combinations
strua = Structure.from_file("a.vasp")
hh=np.arange(512)
combinations_list1 = list(combinations(hh, 2))
print(len(combinations_list1))
combinations_array1 = np.array(combinations_list1)
numberbb = 0
numberaa = 0
for ar in combinations_array1:
ara=strua.copy()
numberbb +=1
print(numberbb)
if ara.get_distance(ar[0],ar[1])>11 or ara.get_distance(ar[0],ar[1])<3:
continue
numberaa +=1
replace_list = [[ar,'O'] ]
for ele in replace_list:
for j in ele[0]:
ara.replace(j,ele[1])
ara.sort()
Vasp_Str = Poscar(ara)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'% numberaa)
2. 检验相同的结构
需要多次分批次检验,否则太慢了,有一个多任务脚本和一个py脚本
在不同文件夹中多次进行多脚本计算,会比较方便

cp ../*new.vasp ./1-first
第一次检验
for i in $(seq 0 1000 130000)
do
cat > job_$i.sh << liz
#!/bin/sh
#SBATCH --job-name=opt
#SBATCH --output=log.out.%j
#SBATCH --error=log.err.%j
#SBATCH --partition=xieyu
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1
source activate liz
python jianyan_$i.py >> jianyan_$i.dat 2>&1
liz
cat > jianyan_$i.py << liz
import os
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.sets import batch_write_input, MPRelaxSet
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
standard_structures= []
dir='/work/home/liz/workspace/3-temporary-duty/2-blue/4-zhengshi/3-B3O-B4O/4-xinzuo/1-替换O/1-str'
for j in range($i,$((i+1000))):
filename = "{}.vasp".format(j)
filepath = os.path.join(dir, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
continue
print(filename)
structure = Structure.from_file(filepath)
standard_structures.append(structure)
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d for d in standard_structures])
print(len(groups))
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups] # 将嵌套列表的每个列表的第一个元素提取出来做成一个新列表
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = $i
for Cry_Str in groupstructures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%dnew.vasp'%n)
liz
sbatch job_$i.sh
done
第二次检验
for i in $(seq 0 10000 130000)
do
cat > job_$i.sh << liz
#!/bin/sh
#SBATCH --job-name=opt
#SBATCH --output=log.out.%j
#SBATCH --error=log.err.%j
#SBATCH --partition=xieyu
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1
source activate liz
python jianyan_$i.py >> jianyan_$i.dat 2>&1
liz
cat > jianyan_$i.py << liz
import os
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.sets import batch_write_input, MPRelaxSet
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
standard_structures= []
dir='/work/home/liz/workspace/3-temporary-duty/2-blue/4-zhengshi/3-B3O-B4O/4-xinzuo/2-去除相同结构/1-first'
for j in range($i,$((i+11000))):
filename = "{}new.vasp".format(j)
filepath = os.path.join(dir, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
continue
print(filename)
structure = Structure.from_file(filepath)
standard_structures.append(structure)
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d for d in standard_structures])
print(len(groups))
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups] # 将嵌套列表的每个列表的第一个元素提取出来做成一个新列表
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = $i
for Cry_Str in groupstructures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%dnew.vasp'%n)
liz
sbatch job_$i.sh
done
最后一步的检验
import os
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.sets import batch_write_input, MPRelaxSet
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
standard_structures= []
dir='/work/home/liz/workspace/3-temporary-duty/2-blue/4-zhengshi/3-B3O-B4O/4-xinzuo/2-去除相同结构/2-new'
for j in range(124000):
filename = "{}new.vasp".format(j)
filepath = os.path.join(dir, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
continue
print(filename)
structure = Structure.from_file(filepath)
standard_structures.append(structure)
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d for d in standard_structures])
print(len(groups))
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups] # 将嵌套列表的每个列表的第一个元素提取出来做成一个新列表
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = 0
for Cry_Str in groupstructures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%dnew.vasp'%n)
3. 替换B原子
先替换B4,再替换B3
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
from itertools import combinations
dir='/work/home/liz/workspace/3-temporary-duty/2-blue/4-zhengshi/3-B3O-B4O/4-xinzuo/2-去除相同结构/2-new'
counter = 0
for j in range(124000):
filename = "{}new.vasp".format(j)
filepath = os.path.join(dir, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
continue
print(filename)
structure = Structure.from_file(filepath)
o_indices = [i for i, site in enumerate(structure) if site.specie.name == "O"]
o_array = np.array(o_indices)
ara=structure.copy()
list1=ara.get_neighbors(ara[o_array[0]], r=2.0)
list2=ara.get_neighbors(ara[o_array[1]], r=2.0)
list1index=np.array([site.index for site in list1])
list2index=np.array([site.index for site in list2])
replace_list = [ [list1index, 'B'] ]
for ele in replace_list:
for j in ele[0]:
ara.replace(j,ele[1])
combinations_list = list(combinations(list2index, 3))
combinations_array = np.array(combinations_list)
for br in combinations_array:
counter += 1
brb=ara.copy()
replace_listara = [ [br, 'B'] ]
for ele in replace_listara:
for j in ele[0]:
brb.replace(j,ele[1])
brb.sort()
Vasp_Str = Poscar(brb)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'% counter)
print(counter)
4. 再次检验相同结构
import os
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.sets import batch_write_input, MPRelaxSet
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
standard_structures= []
dir='/work/home/liz/workspace/3-temporary-duty/2-blue/4-zhengshi/3-B3O-B4O/4-xinzuo/3-替换B'
for j in range(500):
filename = "{}.vasp".format(j)
filepath = os.path.join(dir, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
continue
print(filename)
structure = Structure.from_file(filepath)
standard_structures.append(structure)
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d for d in standard_structures])
print(len(groups))
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups] # 将嵌套列表的每个列表的第一个元素提取出来做成一个新列表
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = 0
for Cry_Str in groupstructures:
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%dnew.vasp'%n)
5. 计算能量,整理结构
rm energy.dat
for i in $(seq 1 1 99);
do
echo -n ${i}new.vasp >> energy.dat
./ewalds.x ../4-去除相同结构/${i}new.vasp -1 0 2 >> energy.dat
done
sort -k3n energy.dat > sorted.dat
mkdir str
cd str
count=1
head -n 100 ../sorted.dat |while read -r line;do
filename=$(echo "$line" | awk '{print $1}')
target_filename=${count}.vasp
cp ../../4-去除相同结构/${filename} ./${target_filename}
count=$((count+ 1))
done
cd ..
3. 替换为B_2O和B_3O的方法
1.枚举氧的结构和其他步骤
2-1. 替换B原子(联合取代、完全枚举)
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
from itertools import combinations
dir='/work/home/liz/workspace/3-temporary-duty/2-blue/4-zhengshi/1-512-B-7-O-2/3-B2O-B3O/1-O-结构'
counter = 0
filename = "1new.vasp"
filepath = os.path.join(dir, filename)
print(filename)
structure = Structure.from_file(filepath)
o_indices = [i for i, site in enumerate(structure) if site.specie.name == "O"]
o_array = np.array(o_indices)
c_indices = [i for i, site in enumerate(structure) if site.specie.name == "C"]
c_array = np.array(c_indices)
ara=structure.copy()
list1=ara.get_neighbors(ara[o_array[0]], r=2.0)
list2=ara.get_neighbors(ara[o_array[1]], r=2.0)
list1index=np.array([site.index for site in list1])
list2index=np.array([site.index for site in list2])
combined_array = np.concatenate((list1index, list2index))
c_array2 = np.setdiff1d(c_array, combined_array)
combinations_list1 = list(combinations(list1index, 2))
combinations_list2 = list(combinations(list2index, 3))
combinations_list3 = list(combinations(c_array2, 2))
array1 = np.array(combinations_list1)
array2 = np.array(combinations_list2)
array3 = np.array(combinations_list3)
print(array3.shape)
print(len(array1))
print(len(array2))
print(len(array3))
for i in range(len(array1)):
for j in range(len(array2)):
for k in range(len(array3)):
brb = ara.copy()
counter += 1
# print(array1[i])
# print(array2[j])
# print(array3[k])
combined_array33=np.concatenate((array1[i], array2[j], array3[k]))
replace_listara = [ [combined_array33, 'B'] ]
for ele in replace_listara:
for m in ele[0]:
brb.replace(m,ele[1])
brb.sort()
Vasp_Str = Poscar(brb)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'% counter)
print(counter)
2-2 先分类再替代
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
from itertools import combinations
dir='/work/home/liz/workspace/3-temporary-duty/2-blue/4-zhengshi/1-512-B-7-O-2/3-B2O-B3O/1-O-结构'
counter = 0
filename = "1new.vasp"
filepath = os.path.join(dir, filename)
print(filename)
structure = Structure.from_file(filepath)
o_indices = [i for i, site in enumerate(structure) if site.specie.name == "O"]
o_array = np.array(o_indices)
c_indices = [i for i, site in enumerate(structure) if site.specie.name == "C"]
c_array = np.array(c_indices)
ara=structure.copy()
list1=ara.get_neighbors(ara[o_array[0]], r=2.0)
list2=ara.get_neighbors(ara[o_array[1]], r=2.0)
list1index=np.array([site.index for site in list1])
list2index=np.array([site.index for site in list2])
combined_array = np.concatenate((list1index, list2index))
print(combined_array)
c_array2 = np.setdiff1d(c_array, combined_array)
combinations_list1 = list(combinations(list1index, 2))
combinations_list2 = list(combinations(list2index, 3))
combinations_list3 = list(combinations(c_array2, 2))
array1 = np.array(combinations_list1)
array2 = np.array(combinations_list2)
array3 = np.array(combinations_list3)
print(array3.shape)
print(len(array1))
print(len(array2))
print(len(array3))
standard_structures=[]
for i in range(len(array1)):
for j in range(len(array2)):
# for k in range(len(array3)):
brb = ara.copy()
# print(array1[i])
# print(array2[j])
# print(array3[k])
combined_array33=np.concatenate((array1[i], array2[j]))
# print(combined_array33)
replace_listara = [ [combined_array33, 'B'] ]
for ele in replace_listara:
for m in ele[0]:
brb.replace(m,ele[1])
standard_structures.append(brb)
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
groups = matcher.group_structures([d for d in standard_structures])
print(len(groups))
groupstructures = [x[0] for x in groups]
for straaa in groupstructures:
for k in range(len(array3)):
copy2=straaa.copy()
counter += 1
replace_listara = [ [array3[k], 'B'] ]
for ele in replace_listara:
for m in ele[0]:
copy2.replace(m,ele[1])
copy2.sort()
Vasp_Str = Poscar(copy2)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'% counter)
print(counter)
2-3 每个结构随机取样特定数目的结构
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
from itertools import combinations
dir='/work/home/liz/workspace/3-temporary-duty/2-blue/4-zhengshi/1-512-B-7-O-2/3-B2O-B3O/1-O-结构'
counter = 0
for j in range(100):
filename = "{}new.vasp".format(j)
filepath = os.path.join(dir, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
continue
print(filename)
structure = Structure.from_file(filepath)
o_indices = [i for i, site in enumerate(structure) if site.specie.name == "O"]
o_array = np.array(o_indices)
c_indices = [i for i, site in enumerate(structure) if site.specie.name == "C"]
c_array = np.array(c_indices)
ara=structure.copy()
list1=ara.get_neighbors(ara[o_array[0]], r=2.0)
list2=ara.get_neighbors(ara[o_array[1]], r=2.0)
list1index=np.array([site.index for site in list1])
list2index=np.array([site.index for site in list2])
combined_array = np.concatenate((list1index, list2index))
c_array2 = np.setdiff1d(c_array, combined_array)
combinations_list1 = list(combinations(list1index, 2))
combinations_list2 = list(combinations(list2index, 3))
combinations_list3 = list(combinations(c_array2, 2))
array1 = np.array(combinations_list1)
array2 = np.array(combinations_list2)
array3 = np.array(combinations_list3)
arr1=np.arange(len(array1))
arr2=np.arange(len(array2))
arr3=np.arange(len(array3))
for ww in range(5000):
np.random.shuffle(arr1)
np.random.shuffle(arr2)
np.random.shuffle(arr3)
brb = ara.copy()
counter += 1
combined_array33=np.concatenate((array1[arr1[1]], array2[arr2[1]], array3[arr3[1]]))
replace_listara = [ [combined_array33, 'B'] ]
for ele in replace_listara:
for m in ele[0]:
brb.replace(m,ele[1])
brb.sort()
Vasp_Str = Poscar(brb)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'% counter)
print(counter)
4.枚举+迭代器进行工作
可以是可以,但是现在太慢了,问题出在挨个去对比结构相似性,一个可行的方案是不断地细分到不同的结构特征集合,用结构特征做一个初筛
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
from itertools import combinations
import itertools
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
strua = Structure.from_file("a.vasp")
hh=np.arange(16,112)
combinations_generator = itertools.combinations(hh, 6)
numberbb = 0
numberaa = 0
all_structure=[]
for ar in combinations_generator:
ara=strua.copy()
numberbb +=1
print(numberbb)
remove_list = list(ar)
ara.remove_sites(remove_list)
ara.sort()
match_found =False
for aa in all_structure:
if matcher.fit(ara,aa):
match_found = True
break
if not match_found:
all_structure.append(ara)
print("%d structures " %len(all_structure))
bb=0
for aa in all_structure:
bb +=1
Vasp_Str = Poscar(aa)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'% bb)
5.枚举-使用静电能作为哈希值而不是fit
这一方法验证错误,因为两个不同的结构可能具有相同的静电能
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
from itertools import combinations
import itertools
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
strua = Structure.from_file("a.vasp")
hh = np.arange(16, 112)
combinations_generator = itertools.combinations(hh, 6)
data = {"Ca":6, "H":-1}
structure_dict = {} # 用于存储已处理的结构
strua.add_oxidation_state_by_element(data)
print(strua)
aaa= 0
for ar in combinations_generator:
aaa +=1
print(aaa)
ara = strua.copy()
remove_list = list(ar)
ara.remove_sites(remove_list)
ara.sort()
# 计算结构的哈希值作为字典的键
ara_hash = EwaldElectrostaticModel().get_energy(ara)
# 使用字典进行匹配检查
if ara_hash not in structure_dict:
structure_dict[ara_hash] = ara
print("New structure added! Total structures: %d" % len(structure_dict))
for Cry_Str in structure_dict.values():
#print(Cry_Str)
Vasp_Str = Poscar(Cry_Str)
n = n+1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'%n)
6. 可以分步骤来做,先替换四个,再替换两个 !
先替换1个,再替换一个,再替换一个,再,,,,这样一定是可以做的
从上往下试,直到能够使用程序做了就停止(95–92),如果从下往上试(92—95)会面临文件数太多的困难
5.检验
1. 逐个检验相似性
import numpy as np
import sys,os,time
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
all_str = []
for i in range(1,100000):
file = f'{i}.vasp'
if not os.path.exists(file):
continue
print(file)
strua = Structure.from_file(file)
match_found = False
for str in all_str:
if matcher.fit(strua,str):
match_found = True
break
if not match_found:
all_str.append(strua)
print('%d structures' % len(all_str))
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
n = 0
for strua in all_str:
Vasp_Str = Poscar(strua)
n +=1
Vasp_Str.write_file('%dnew.vasp'%n)
2. 检验两个结构
import numpy as np
import sys,os,time
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher
matcher = StructureMatcher()
aa = Structure.from_file('16.vasp')
bb = Structure.from_file('4199.vasp')
matcher.fit(aa,bb)
7.找出缺失的原子
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from itertools import combinations
stru_b=Structure.from_file(filename='supercell.vasp')
frac_coords_b=stru_b.frac_coords.tolist()
normalized_coords_b = [[x % 1 for x in coord] for coord in frac_coords_b]
set2 = set(map(tuple, normalized_coords_b))
for i in range(1, 1000001):
file = f'{i}.vasp'
stru_a=Structure.from_file(file)
# 检查文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(file):
continue
frac_coords_a=stru_a.frac_coords.tolist()
normalized_coords_a = [[x % 1 for x in coord] for coord in frac_coords_a]
set1 = set(map(tuple, normalized_coords_a))
result= [list(i) for i in set2.difference(set1)]
print(result)
atom_indices=[]
for coord in result:
try:
index = normalized_coords_b.index(coord)
atom_indices.append(index)
except ValueError:
# 如果找不到匹配的坐标,可以添加一个标记,如-1,以表示未匹配的坐标
atom_indices.append(-1)
close_atom_pairs = []
combinations_of_missing_atoms = combinations(atom_indices, 2)
threshold_distance = 7
for pair in combinations_of_missing_atoms:
distance = stru_b.get_distance(pair[0], pair[1])
if distance < threshold_distance:
close_atom_pairs.append(pair)
# 如果 close_atom_pairs 列表不为空,则表示存在距离小于阈值的原子对
if close_atom_pairs:
print("存在距离小于阈值的原子对:")
print(len(close_atom_pairs))
else:
print("不存在距离小于阈值的原子对。")
7. 处理CaH6的333倍胞的问题(将324个H中的14个扣掉-可以枚举的方法
==/work/home/liz/workspace/3-temporary-duty/3-zwb/6-333/1-kou3/2/1-2/ee.py==
from pymatgen.core.structure import IStructure, Structure
from pymatgen.io.vasp.inputs import Poscar
from monty.io import zopen
import random
import sys,os,time
import numpy as np
from pymatgen.core import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.energy_models import EwaldElectrostaticModel
from itertools import combinations
strua = Structure.from_file("a.vasp")
H_indice = [i for i, site in enumerate(strua) if site.species_string == "H"]
H_indices=np.array(H_indice)
distanceall=strua.distance_matrix
distance=distanceall[H_indices][:,H_indices]
print(distance.shape)
print(distance)
N = distance.shape[0]
two_dim_matrix = np.zeros((N, N), dtype=int)
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
dist1 = distance[i][j]
if dist1 <= 3.6:
two_dim_matrix[i][j] = 0
else:
two_dim_matrix[i][j] = 1
allnumber = 0
matching_columns = np.where(two_dim_matrix[0, 1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns = matching_columns + 1
print(matching_columns)
for j in matching_columns:
print(j)
matching_columns2=np.where(two_dim_matrix[j, j+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns2 = matching_columns2 + j + 1
matching_columns2 = np.intersect1d(matching_columns2,matching_columns)
# print(len(matching_columns2))
for jj in matching_columns2:
matching_columns3=np.where(two_dim_matrix[jj, jj+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns3 = matching_columns3 + jj + 1
matching_columns3 = np.intersect1d(matching_columns2,matching_columns3)
# print(len(matching_columns3))
for jjj in matching_columns3:
matching_columns4=np.where(two_dim_matrix[jjj, jjj+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns4 = matching_columns4 + jjj + 1
matching_columns4 = np.intersect1d(matching_columns3,matching_columns4)
# print(len(matching_columns4))
for jjjj in matching_columns4:
matching_columnsddd=np.where(two_dim_matrix[jjjj, jjjj+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columnsddd = matching_columnsddd + jjjj + 1
matching_columnsddd = np.intersect1d(matching_columns4,matching_columnsddd)
# print(len(matching_columnsddd))
for gg in matching_columnsddd:
matching_columns5=np.where(two_dim_matrix[gg, gg+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns5 = matching_columns5 + gg + 1
matching_columns5 = np.intersect1d(matching_columnsddd,matching_columns5)
# print(len(matching_columns5))
for ggg in matching_columns5:
matching_columns6=np.where(two_dim_matrix[ggg, ggg+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns6 = matching_columns6 + ggg + 1
matching_columns6 = np.intersect1d(matching_columns5,matching_columns6)
# print(len(matching_columns6))
for gggg in matching_columns6:
matching_columns7=np.where(two_dim_matrix[gggg, gggg+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns7 = matching_columns7 + gggg + 1
matching_columns7 = np.intersect1d(matching_columns6,matching_columns7)
# print(len(matching_columns7))
for dd in matching_columns7:
matching_columns8=np.where(two_dim_matrix[dd, dd+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns8 = matching_columns8 + dd + 1
matching_columns8 = np.intersect1d(matching_columns7,matching_columns8)
# print(len(matching_columns8))
for ddd in matching_columns8:
matching_columns9=np.where(two_dim_matrix[ddd, ddd+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns9 = matching_columns9 + ddd + 1
matching_columns9 = np.intersect1d(matching_columns8,matching_columns9)
# print(len(matching_columns9))
for dddd in matching_columns9:
matching_columns10=np.where(two_dim_matrix[dddd, dddd+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns10 = matching_columns10 + dddd + 1
matching_columns10 = np.intersect1d(matching_columns9,matching_columns10)
# print(len(matching_columns10))
for ww in matching_columns10:
matching_columns11=np.where(two_dim_matrix[ww, ww+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns11 = matching_columns11 + ww + 1
matching_columns11 = np.intersect1d(matching_columns10,matching_columns11)
# print(len(matching_columns11))
for www in matching_columns11:
matching_columns12=np.where(two_dim_matrix[www, www+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns12 = matching_columns12 + www + 1
matching_columns12 = np.intersect1d(matching_columns11,matching_columns12)
# print(len(matching_columns12))
for wwww in matching_columns12:
matching_columns13=np.where(two_dim_matrix[wwww, wwww+1:] == 1)[0]
matching_columns13 = matching_columns13 + wwww + 1
listaaa=[0,j,jj,jjj,jjjj,gg,ggg,gggg,dd,ddd,dddd,ww,www,wwww]
# print(listaaa)
allnumber += 1
#print(allnumber)
# print(listaaa)
if allnumber % 100000 == 0:
print(allnumber)
print(listaaa)
listbbb= H_indices[listaaa]
print(listbbb)
ara=strua.copy()
for ele in listbbb:
ara.replace(ele,'O')
ara.sort()
Vasp_Str = Poscar(ara)
Vasp_Str.write_file('%d.vasp'% allnumber)
# for wwwww in matching_columns14:
# matching_columns15=np.where(two_dim_matrix[wwwww, wwwww+1:] == 1)[0]
# matching_columns15 = matching_columns15 + wwwww + 1




转载请注明来源 有问题可通过github提交issue