6. 计算RDF(径向分布函数)
1. 理论知识
1.https://bohrium.dp.tech/notebooks/7293
2.知乎 径向分布函数Radial distribution function - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
1.2: Radial Distribution Function - Chemistry LibreTexts


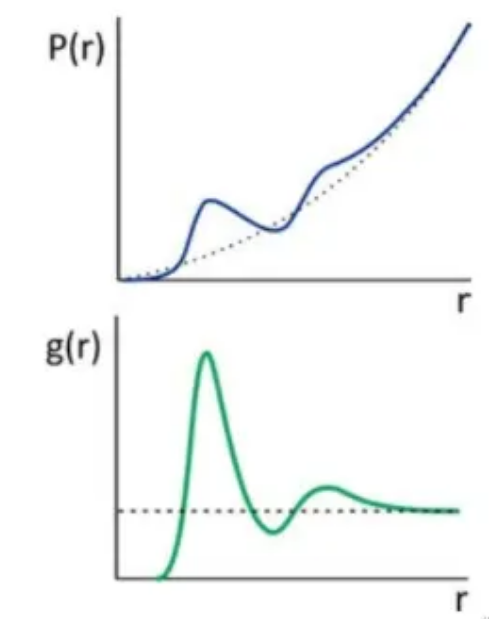
这里的平均粒子数密度既包括了时间平均,也包括了对不同位置处的平均

3. 课本复杂版本 J.M.HAILE molecular dynamics simulation ==page 260==
g(r)正比于发现原子对为r的两个原子的概率
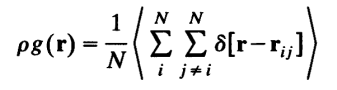
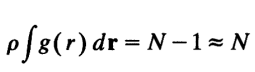
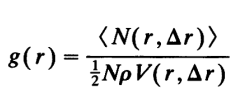

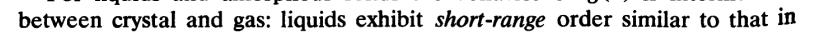


1. OVITO
2. 脚本
1. fortran
!November 10, 2015 by Peihao Huang --<<Computer simulation of liquids>> page 183
program main
implicit none
integer ::k,i,j,Natoms,step,Nstep,n,n1,n2,BIN,MAXBIN,reject,Nreject
real(kind=8) ::factor,a(3,3),r1,r2,r3,Rx,Ry,Rz,Rsq,R,DELR,RMAX,CONST,RHO,RLOWER,RUPPER,NIDEAL,RMIDDLE,Volume,Total,Coor,Rmin
real(kind=8),allocatable ::x(:),y(:),z(:),GR(:)
integer,allocatable ::HIST(:)
real,parameter ::PI=3.14159265
!These parameters should be input by hand
DELR=0.1 !间距?不用改
RMAX=5.9 !最小晶格常数的一半
Nreject=6000 !去掉的步数
Nstep=10477 !剩下的步数
!Initialize
MAXBIN=INT(ANINT(RMAX/DELR))
allocate(HIST(MAXBIN))
allocate(GR(MAXBIN))
do k=1,MAXBIN
HIST(k)=0
end do
!Read the structural information
open(unit=10,file='XDATCAR_300GPa_2300K')
read(10,*)
read(10,*)factor
read(10,*)a(1,1),a(1,2),a(1,3)
read(10,*)a(2,1),a(2,2),a(2,3)
read(10,*)a(3,1),a(3,2),a(3,3)
do i=1,3
do j=1,3
a(i,j)=a(i,j)*factor
end do
end do
read(10,*)
read(10,*)Natoms
allocate(x(Natoms))
allocate(y(Natoms))
allocate(z(Natoms))
!Calculate the average density of the system
Volume=a(1,2)*a(2,3)*a(3,1)+a(1,3)*a(2,1)*a(3,2)+a(1,1)*a(2,2)*a(3,3)-a(1,3)*a(2,2)*a(3,1)-a(1,1)*a(2,3)*a(3,2)-a(1,2)*a(2,1)*a(3,3)
RHO=REAL(Natoms)/Volume
write(*,*)"The total Volume is ",Volume
!Reject some steps before equilibrium
do reject=1,Nreject
read(10,*)
do n=1,Natoms
read(10,*)
end do
end do
!Read the equilibrium steps
do step=1,Nstep
read(10,*)
do n=1,Natoms
read(10,*)x(n),y(n),z(n)
end do
do n1=1,Natoms-1
do n2=n1+1,Natoms
!Calculate minimum image distances
r1=x(n2)-x(n1)
r1=r1-ANINT(r1)
r2=y(n2)-y(n1)
r2=r2-ANINT(r2)
r3=z(n2)-z(n1)
r3=r3-ANINT(r3)
!Fractional to cartesian
Rx=r1*a(1,1)+r2*a(2,1)+r3*a(3,1)
Ry=r1*a(1,2)+r2*a(2,2)+r3*a(3,2)
Rz=r1*a(1,3)+r2*a(2,3)+r3*a(3,3)
Rsq=Rx**2+Ry**2+Rz**2
R=SQRT(Rsq)
!Sort the distances between the N atoms into histogram
BIN=INT(R/DELR)+1
if(BIN<=MAXBIN) then
HIST(BIN)=HIST(BIN)+2
end if
end do
end do
end do
!Normalize
CONST=4.0*PI*RHO/3
do BIN=1,MAXBIN
RLOWER=REAL(BIN-1)*DELR
RUPPER=RLOWER+DELR
NIDEAL=CONST*(RUPPER**3-RLOWER**3)
GR(BIN)=REAL(HIST(BIN))/REAL(Nstep)/REAL(Natoms)/NIDEAL
end do
close(10)
!Write
open(unit=20,file='rdf.dat')
do BIN=1,MAXBIN
RMIDDLE=REAL(BIN-1)*DELR+DELR/2
write(20,*)RMIDDLE,GR(BIN)
end do
close(20)
!Check (RMAX should be set to sqrt(3)/2*L for cubic box)
Total=0
do BIN=1,MAXBIN
RLOWER=REAL(BIN-1)*DELR
RUPPER=RLOWER+DELR
NIDEAL=CONST*(RUPPER**3-RLOWER**3)
Total=Total+GR(BIN)*NIDEAL
! Total=Total+RHO*4*PI*(DELR*BIN)**2*GR(BIN)*DELR #this one is less accurate
end do
write(*,*)"The total number of atoms is ",Total
!Calculate coordination number (method1: input by hand)
Coor=0
do BIN=1,44
RLOWER=REAL(BIN-1)*DELR
RUPPER=RLOWER+DELR
NIDEAL=CONST*(RUPPER**3-RLOWER**3)
Coor=Coor+GR(BIN)*NIDEAL
Rmin=REAL(BIN-1)*DELR+DELR/2
end do
write(*,*)"The coordination number is ",Coor,",and rmin is ",Rmin
!(method 2)
Coor=0
do BIN=1,MAXBIN
RLOWER=REAL(BIN-1)*DELR
RUPPER=RLOWER+DELR
NIDEAL=CONST*(RUPPER**3-RLOWER**3)
Coor=Coor+GR(BIN)*NIDEAL
Rmin=REAL(BIN-1)*DELR+DELR/2
if((BIN>1).and.(BIN<MAXBIN).and.(GR(BIN)<GR(BIN-1)).and.(GR(BIN)<GR(BIN+1))) then
write(*,*)"The coordination number is ",Coor,",and rmin is ",Rmin
exit
end if
end do
deallocate(x)
deallocate(y)
deallocate(z)
deallocate(HIST)
deallocate(GR)
end program main
2. python (ovito )
conda下载ovito用官方的软件源(官方网址中有)不用conda-forge (官方python有付费版功能,conda源版没有)
##write by lijiaxiang
# example script for calculating and plotting RDFs and partial RDFs
# CAN NOT BE USED DIRECTLY!
# modify and run this script.
# add plt.savefig('fig') if you want to save the RDF figures.
# # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # #
from ovito.io import import_file, export_file
from ovito.modifiers import CoordinationAnalysisModifier, TimeAveragingModifier
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
def get_data(strj_path: str, partial=False):
pipeline = import_file(strj_path)
modifier = CoordinationAnalysisModifier(cutoff=6, number_of_bins=200, partial=partial)
pipeline.modifiers.append(modifier)
pipeline.modifiers.append(TimeAveragingModifier(operate_on='table:coordination-rdf'))
export_file(pipeline, "rdf.txt", "txt/table", key="coordination-rdf[average]")
with open('./rdf.txt', 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
title = lines[1]
lines = lines[2:]
lines = [i.split() for i in lines]
datas = np.array(lines)
datas = datas.astype(float)
labels = title.split('"')[-1].split()
os.remove('./rdf.txt')
# sort
labels = ["-".join(sorted(i.split('-'))) for i in labels]
sorts = sorted(enumerate(labels), key=lambda x: x[1])
labels = [item[1] for item in sorts]
sorted_indices = [item[0] for item in sorts]
datas = datas[:, [0] + [i + 1 for i in sorted_indices]]
return datas, labels
def is_in(nplot: list, label: str):
for i in nplot:
if i in label:
return True
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
cm = plt.colormaps['Paired']
# get rdf
datas_vasp, labels_vasp = get_data('/Users/spook/Desktop/h2o/XDATCAR')
datas_ml, labels_ml = get_data('/Users/spook/Desktop/h2o/A.lammpstrj661')
# plot rdf -------------------------------------------------------------------
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4, 3), dpi=200)
ax = fig.add_subplot()
ax.plot(datas_vasp[:, 0], datas_vasp[:, 1], label="DFT")
ax.plot(datas_ml[:, 0], datas_ml[:, 1], linestyle="--", c='r', label="ACNN")
ax.set_xlabel('r')
ax.set_ylabel('g(r)')
ax.set_title('RDF')
y_lim = ax.get_ylim()
ax.set_ylim(y_lim[0], 10)
ax.legend()
# rdf plot end --------------------------------------------------------------
#
#
#
"""
1. get partial rdf
2. plot partial rdf. The `include (list)` denote the elements or bonds to be plot.
eg: ["H"] plot all bonds contain "H" atoms.
["H-O"] plot "H-O" rdf only.
["Ti", "H-O"] plot "Ti" rdf adding "H-O"
"""
# get partial rdf
datas_vasp, labels_vasp = get_data('/Users/spook/Desktop/h2o/XDATCAR', partial=True)
datas_ml, labels_ml = get_data('/Users/spook/Desktop/h2o/A.lammpstrj661', partial=True)
# plot partial rdf -----------------------------------------------------------
include = ['Ti']
include = ["-".join(sorted(i.split('-'))) for i in include]
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4), dpi=200)
ax = fig.add_subplot()
for i in range(len(labels_vasp)):
if is_in(include, labels_vasp[i]):
ax.plot(datas_vasp[:, 0], datas_vasp[:, 1 + i], c=cm.colors[i], label="DFT " + labels_vasp[i], linewidth=1)
for i in range(len(labels_ml)):
if is_in(include, labels_ml[i]):
ax.plot(datas_ml[:, 0], datas_ml[:, 1 + i], c=cm.colors[i], label="ACNN " + labels_ml[i], linestyle="--",
linewidth=2)
ax.set_xlabel('r')
ax.set_ylabel('g(r)')
ax.set_title('RDF ' + " ".join(include))
ax.legend(ncol=2, prop={'size': 8})
转载请注明来源 有问题可通过github提交issue